Compound
Compound for insulation of electric wires and cables (PE-Xb)
CROSSLINKED POLYETHYLENE (PE-Xb) used for insulation of electrical cables for low/medium and high voltage.
Characteristics :
Despite the excellent electrical properties of the polyethylene, the low melting temperature limits its application at 70 ° C. In case of overheating due to overloads or short circuits, the polyethylene may melt leaving the conductor exposed .
The addition of specific agents (peroxides, silanes) at low density polyethylene allows, under certain circumstances, crosslink the material resulting in the creation of a tridimensional structure with new connections between the long molecular chains. The SIOPLAS technology used for crosslinking was developed by Dow Corning and called SIOPLAS:
The process of crosslinking substantially improves the stability of the mechanical characteristics under temperature variation. The maximum working temperature goes to 90°C and under short-circuited to 250°C, increasing the resistance to abrasion, impact, cracking and chemical resistance. The crosslinking is also improve the performance at low temperatures, reducing the shrinkage of the material.
Due the electrical properties of the crosslinked polyethylene not differ significantly from polyethylene, the excellent insulating characteristics remains, which allows to reduce the thickness of the insulation when compared to PVC. This feature, beside the fact of polyethylene have low-halogen, low opacity and corrosiveness of fumes released in its combustion, makes the cross-linked insulation material suitable for low voltage power cables.
As properties stand out even good heat resistance, good flexibility, good resistance to ozone.
Compared with other crosslinking processes, the silane method proves to be the best cost-effective relationship, requiring no investment in expensive equipment such as electron accelerators or continuous vulcanization.
- n addition, the technology enables high speeds silane and the extrusion process starts with less material loss.
- Even with low density cross-linked three-dimensional network structure allows obtaining the desirable mechanical properties.
- The aging resistance of PEX obtained by addition of silane is higher than that obtained via process by radiation or peroxide addition.
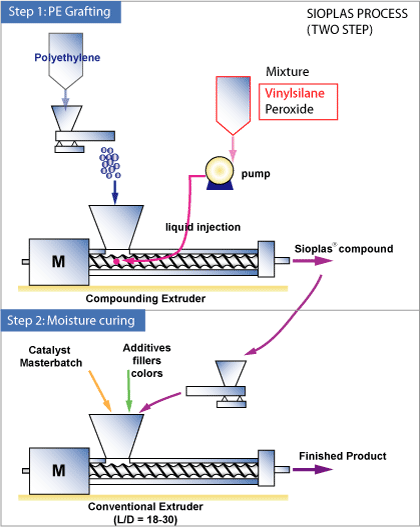
The main disadvantage of this method is that the use of silane requires a two-step process, that is, the silane grafting of polyethylene in the molecule and condensation of silanol group in which the temperature and presence of water (that has to diffuse through the polymer) is required.
- Silane Grafted Crosslinkable Polyethylene for Low Voltage Power Cable Insulation Grade – PP 408/401
- Silane Grafted Crosslinkable Polyethylene for Medium and High Voltage Power Cable Insulation Grade – PP 409/401
- Silane Grafted Crosslinkable Polyethylene Black for Low Voltage Power Cable Insulation / Sheath Grade – XL-ABC-01
- Thermoplastic Semiconductive Compound for Conductor/Insulation Shielding of Power Cables